


| Pair Name | Curcumin, Vemurafenib | ||
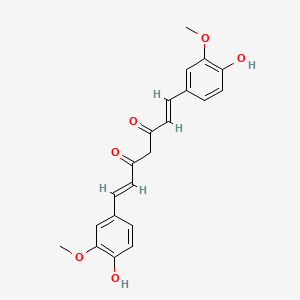
| Phytochemical Name | Curcumin (PubChem CID: 969516 ) | ||
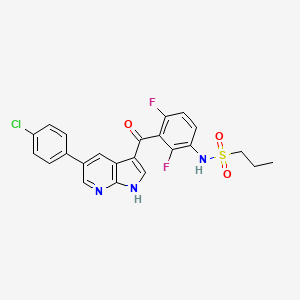
| Anticancer drug Name | Vemurafenib (PubChem CID: 42611257 ) | ||
| Structure of Phytochemical |
|
Download
2D
MOL
3D
MOL
|
|
| Structure of Anticancer Drug |
|
Download
2D
MOL
3D
MOL
|
|
| Pair Name | Curcumin, Vemurafenib | |||
| Disease Info | [ICD-11: 2C30] | Melanoma | Investigative | |
| Biological Phenomena | Induction-->Apoptosis | |||
| Gene Regulation | Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | EGFR | hsa1956 |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | AKT1 | hsa207 | |
| Down-regulation | Phosphorylation | MAPK1 | hsa5594 | |
| Up-regulation | Expression | ROS1 | hsa6098 | |
| In Vitro Model | A375.S2 | Amelanotic melanoma | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0136 |
| Result | Curcumin suppresses cell proliferation and triggers apoptosis in vemurafenib-resistant melanoma cells by downregulating the EGFR signaling pathway | |||
| No. | Title | Href |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Curcumin suppresses cell proliferation and triggers apoptosis in vemurafenib-resistant melanoma cells by downregulating the EGFR signaling pathway. Environ Toxicol. 2022 Apr;37(4):868-879. doi: 10.1002/tox.23450. | Click |
